Web
The web is the front-end for the Kerberos Open Source agent, it allows you to review recordings and update camera settings.
Kerberos Open Source is deprecated, please use Kerberos Agent instead.
The web is responsible for the visualization. It’s a GUI which helps the user to find activity at a specific period, configure the machinery, view a live stream, see system information and much more.
It’s written in PHP using the extremely popular PHP Framework Laravel, and Javascript using the client-side framework BackboneJS. We will discuss the different pages and functionality briefly. Please check out the demo environment if you want to see a real life example.
Overview
We will shortly discuss the different pages that make up the web interface of Kerberos Open Source.
Dashboard
The landing page of the web is the dashboard. On the dashboard a user will see some statistics: activity per hour, activity per day, a live stream, the latest activity and a heatmap.
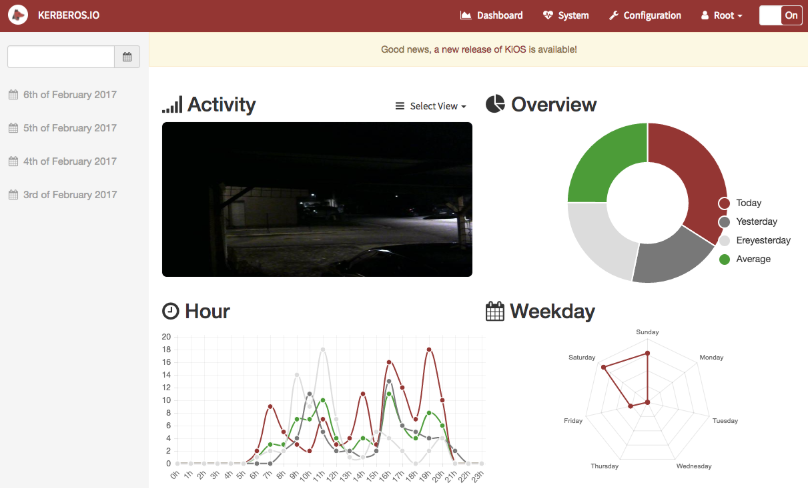
The dashboard gives a high-level overview of your Kerberos Opensource agent.
Overview
When selecting a specific day, you’ll will get a timeline and overview. By using the timeline you can navigate through a day; the timeline highlights the amount of activity, from gray to red.
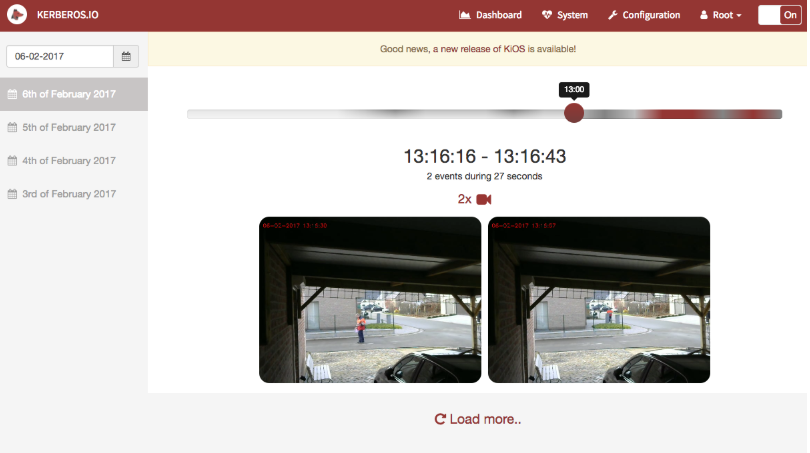
The media page gives an overview of your recordings (grouped into sequences) for that specific day.
Settings
The settings page allows you to configure the machinery. You can define the type of camera, post-processes, conditions and much more; it’s highly configurable.
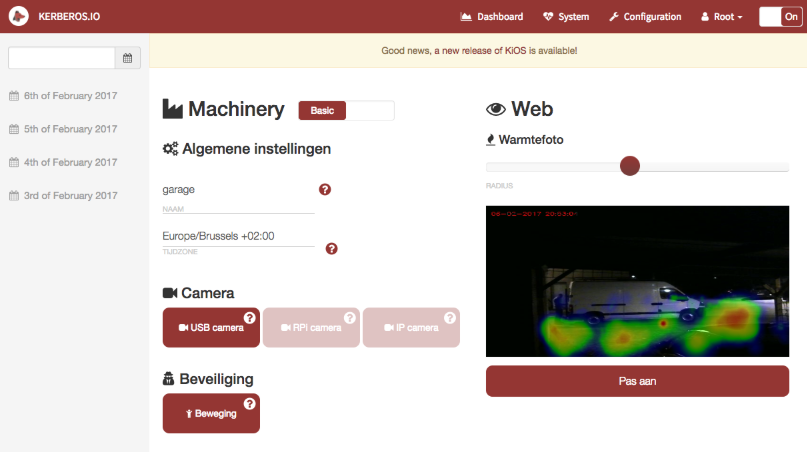
The settings page allows you to modify and tweak the camera and motion settings.
System
The system page allows you to monitor the system. On this page you’ll get an overview of the system specifications (CPU, Memory, Network, etc). Several actions are available: you can download system information (for debugging purposes) and download or remove your images.
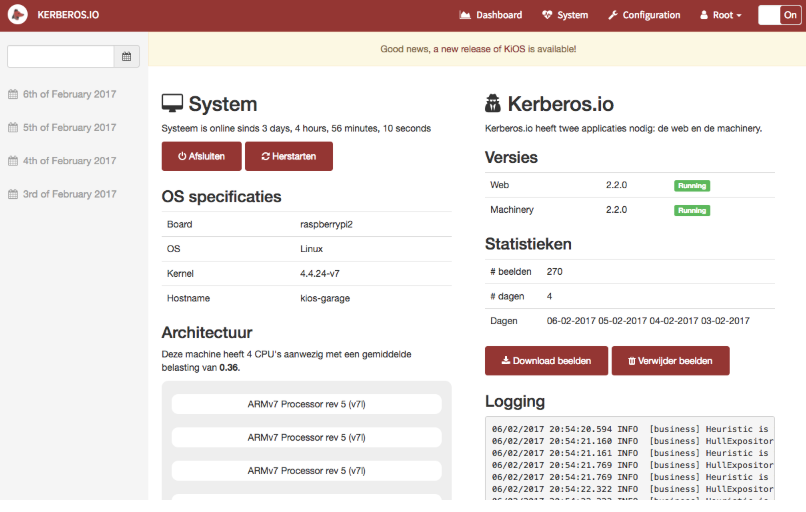
The system pages show you the current status of your agent.
Project structure
The web interface is using the Laravel framework (version 5.4). There is a lot of documentation related to Laravel, please review their documentation website here. In a nutshell this is how the web is organised.
Back-end
- config/app.php - general application settings.
- config/kerberos.php - this file contains web specific parameters; the user credentials to sign in, etc.
- app/Http/Controllers - MVC controllers
- app/Http/Repositories -repositories are injected into the controller.
- app/Providers/AppServiceProvider.php - bind repositories to a specific interface - dependency injection.
- routes/api.php - contains all the URI endpoints for Ajax calls.
- routes/web.php - url routing for pages.
Front-end
- public/css/less - LESS is used for the CSS.
- public/js/app - BackboneJS and RequireJS is used for building modular JS classes.
- public/js/mustache - Mustache is used for the client-side view rendering.
- public/js/vendor - This is where the bower extensions are installed.
- public/capture - A directory where images are written to by default.
- public/bower.json - The bower extensions used in the web repository.
- public/Gruntfile.js - We are using Grunt for our task manager.
API
If you want to integrate the Kerberos agent with your own application, you’re at the right place! The web interface comes with a RESTfull API, that allows you to retrieve and modify information from the Kerberos agent.
- Disable the machinery
- Health check
- Enable or disable output devices
- etc.
Authentication
To use the RESTfull API of your Kerberos agent you need to define an Authorization header with each request. We use Basic Authentication to secure the different endpoints.
"Authorization": "Basic root:root"
An example with Python looks like this.
import requests
import json
import base64
url = "http://ip-of-pi/api/v1/condition/enabled"
username = "user"
password = "passw"
basicAuth = base64.b64encode('%s:%s' % (username, password))
headers = {"Authorization": "Basic " + basicAuth, "Content-Type": "application/json"}
data = '{"active": "true"}'
#Call REST API
response = requests.put(url, data=data, headers=headers)
print(response.text)
If you’re using the wrong credentials, the web will return following error message.
Invalid credentials.
Endpoints
All endpoints are prefixed with api/v[version]/, in which the last part defines the API version number. Below you will find all the available endpoints with there signature and response. Note that when you call an endpoint which doesn’t exists, the web will throw an 404.
{
"error": "API method does not exists"
}
Version 1
Below you’ll find a list of all API methods which are available for version 1.
GET api/v1/name
Description
Retrieve the name of your instance.
Response
{
"name": "frontdoor"
}
PUT api/v1/name
Description
Change the name of your instance.
Payload
{
"name": "frontdoor-changed"
}
Response
{
"name": "frontdoor-changed"
}
GET api/v1/images/latest_sequence
Description
Retrieve the latest sequence detected.
Response
[
{
"time": "10:59:57",
"src": "https://demo.kerberos.io/capture/1501491597_6-310145_frontdoor_722-691-873-926_703_511.mp4",
"local_src": "/var/www/web/public/capture/1501491597_6-310145_frontdoor_722-691-873-926_703_511.mp4",
"metadata": {
"key": "1501491597_6-310145_frontdoor_722-691-873-926_703_511.mp4",
"user": "1501491597_6-310145_frontdoor_722-691-873-926_703_511.mp4",
"timestamp": 1501491597,
"microseconds": "6-310145",
"instanceName": "frontdoor",
"regionCoordinates": "722-691-873-926",
"numberOfChanges": "703",
"token": "511"
},
"type": "video"
}
]
GET api/v1/condition/enabled
Description
Check if enabled or disabled.
Response
{
"active": "true",
"delay": "5000"
}
PUT api/v1/condition/enabled
Description
Activate or disable the system.
Payload
{
"active": "false"
}
Response
{
"active": "false",
"delay": "5000"
}
GET api/v1/system/health
Description
Check if the machinery is running (the stream is connected).
Response
{
"status": "false"
}
 Kerberos Docs
Kerberos Docs